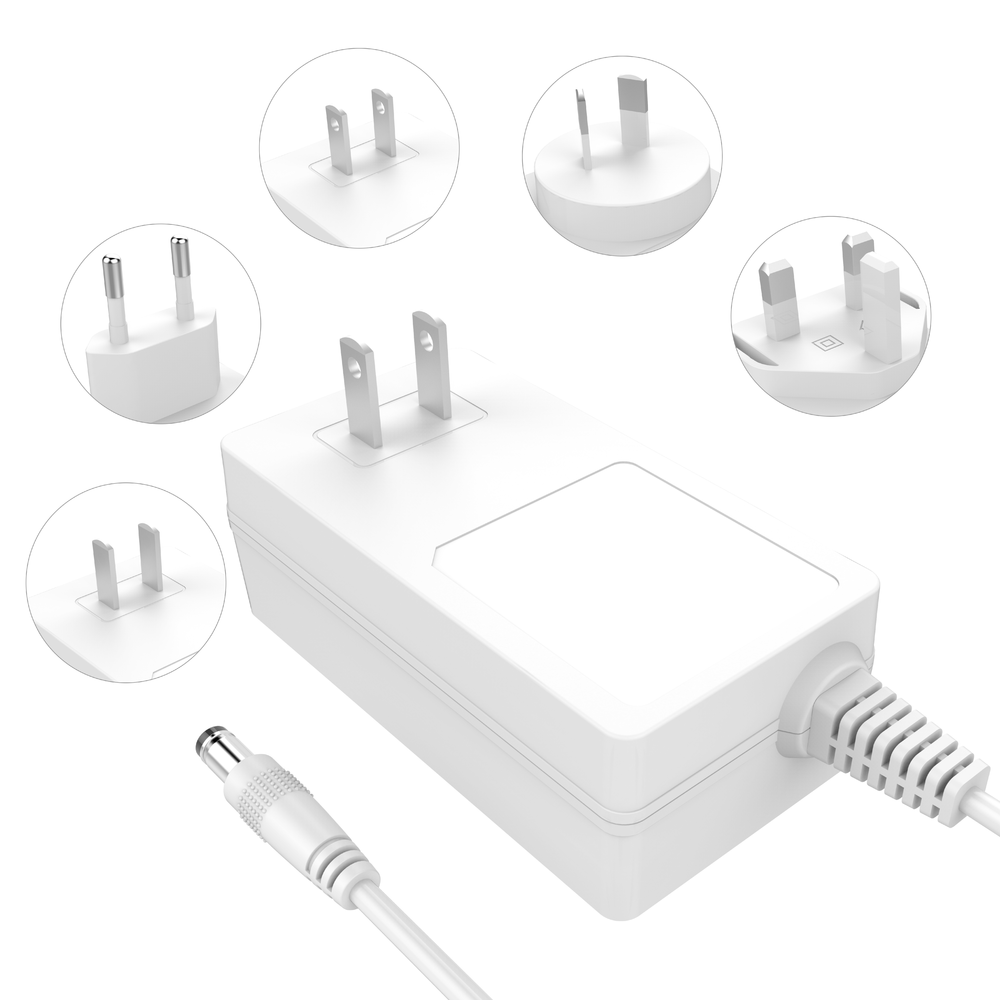
Optical fiber welding machine operation and optical power meter
by:Tumtec
2020-04-15
Operating the relationship between the optical fiber welding machine and optical power meter operating the relationship between the optical fiber welding machine and optical power meter, power monitoring technology by light power transfer to determine the best optical fiber alignment through the joining together of point source, in the light wavelength system, connected to the input end of the fiber.
The emission of light through the joining together of points, and detected by the optical power meter on the output end.
Optical alignment is passed, until a maximum power readings move in X and Y on the transverse direction of optical fiber.
This alignment method needs a person to monitor the output power level, and a communication link to the individual operating optical fiber welding machine.
This method is applicable to the multimode and single-mode fiber, is the improvement in the visual alignment, because it's best to aim at rather than the cladding optical fiber core.
Optical fiber can also use the OTDR aim instead of remote power meter as power calibration method.
Aim OTDR, however, depends on the OTDR, in order to provide appropriate real-time display of stitching orientation ability of optimization.
An alternative approach is the use of partial injection and detection,
盖子)
System, which is in a lot of welding machine.
Essence, the cover is a power on the system since the site is included in the fusion.
Cover to eliminate the need of remote monitoring;
In on both sides of the optical fiber splicing point is around a cylindrical mandrel is small enough, to allow for the bending of light injection through optical fiber coating on the input side, and detection on the output side.
Data on the system said another method of the fiber orientation.
Collimating light through the optical fiber orientation Angle of optical axis, the splicing point itself, can be brought into alignment of optical fiber image is produced.
Some outline on the centerline of the unit to create core computer generated images, the computer bring alignment before fusion.
Other activities configuration of using the optical fiber cladding aligned arrangement of unit of personal data.
However, alignment depends on the quality of the core/cladding concentricity.
Fixed V groove alignment technology, passive optical fiber orientation is the result of the precise processing V groove and precise control of the optical fiber cladding diameter and core/cladding concentricity.
Fusing once optical fiber is the best alignment, fusion process can be initiated.
However, the existing fusion, one or more of the short arc current pulse sequence is generally used to from the fiber end to remove any contaminants.
In some units, this step can be included in the normal cycle of fusion.
In the next step in the process of fusion is called integration.
In front of the fusion step, fiber end heat softening add fiber end.
This ensures that the optical fiber end is in the best temperature fusion in the subsequent steps, so that the optical flow (
Melt)
In the physical contact together.
High melting temperature of lead to excessive deformation and may change the glass fiber end?
吗?
Geometry, to produce the poor quality of splicing.
Before, on the other hand, low fusion temperature may cause fiber end of mechanical deformation and subsequent buckling as the optical fiber end in the fusion steps together.
Best optical fiber temperature distribution in the fusion and the influence of the final fused arc parameters (
Arc current and time)
Before, and the time period of optical fiber end remains separate physical contact.
From previously and the method of fusion splicing changes to splice, they can be divided into two main categories: gradual or sudden preheating.
Methods melting in advance to determine the thermal distribution uniformity on the fiber end face.
Gradually or step before fusion (
Figure 3)
Achieving a uniform heating of the optical fiber end face and the burst forecast fusion focused on very hot end of flange on the optical fiber causes a chamfer effect;